The Vascular Podiatrist
Taking a good clinical history is vital together with social history. We cover limb oedema (swelling) and changes in the skin with the effects of poor supply. The ultrasound Doppler and blood pressure tests in arms, ankles and toes are vital to match clinical findings with factual changes in pulse quality, pressures and the types of waves. All this information can make a prediction as to the risk associated with vascular disease from amputations to aneurysms to clots and thickening of the walls of blood vessels.
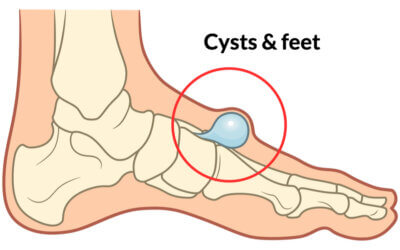
Understanding ganglions in feet
The nuisance factor behind ganglia and swellings is the potential for pain associated with trapped nerves producing sharp electric shock pains that can shoot into the foot or up the leg. Infections are not common but cause ascending pain and must be investigated and managed. Deeper bursae do well from injections where they form part of normal anatomy. These are called an anatomical bursa. Tethered down with strapping can help or they can be protected by foam and gel padding.
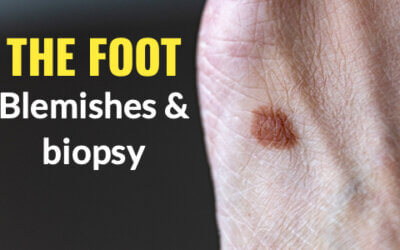
Biopsy in the foot
There are several techniques available to the surgeon. We can shave the top to acquire a sample or we can punch a section out using a small punch. The last technique is excisional biopsy, often used as part of treatment. Shave, punch and excisional biopsy are the different techniques. Biopsy is designed as a diagnostic method of test for abnormal skin cells.
Biomechanics and the foot orthosis
In the USA, from the sixties, the earlier designs were based around a popular subject called ‘biomechanics’. This was a pseudo term but became a significant part of the podiatric medicine degree course in the USA. Much of this pseudo-science involved measurements with protractors (tractographs) and in build error ‘eyesight’ assessment which led to assumptions with a predilection for the concept of wedging. The foot orthosis (F.O.), as it was called, tried to separate itself from the older insole and appliance. A google search today will still confuse the terms.
Guide to Contents
I have created a contents page to provide a guide. You can also use the search tool as well.
Smelly feet and the home truth
Poor hygiene adds to the build-up of skin squares offering greater bacterial opportunity. However, increased sweating requires increased temperature, exercise and stress affected by medical drugs and chemicals as in foods. Increased sweating may require medical intervention. One condition that is less common is pitted keratolysis; lysis means breaking down.
A career in Podiatric Medicine
Most podiatrists are only too happy to speak to school leavers and students about the profession of podiatry. Contact the practice and ask if you can attend a clinic
Podiatry as a career choice?
Like a flying carpet from the Arabian Nights of old, I was transformed along a landscape that threw up new opportunities; it was an unchartered journey, unlike today. Like many friends and colleagues, I did not leave school knowing about podiatry. Our career’s office at school failed to mention this, and I was heading for a failed destiny. By chance, I was redirected as many have been.
Avoiding Death by PowerPoint
Well, it is simple. Good speakers feel that PowerPoint makes people lazy, leading to a lack of being prepared. I thought it was a good topic as conference season is starting to warm up for some. Preparation is everything and of course, your talk looks better for those slides. I am a strong proponent of PowerPoint, but I have to say it is poorly used more than it is used well. In preparing this short article I have adopted the term Death by PowerPoint because it really can kill what could be a good talk. A few tips might not go amiss.
Foot cramp is there a cause?
Salt is not just sodium chloride but calcium, potassium, magnesium. These chemicals are also known as electrolytes which are important for nerve conduction and health muscle function. One myth cramp was to eat a banana because this had potassium, a significant body salt. Athletes had their blood levels measured based on their loss of water in sweat and, hence, salt loss. The findings showed little difference between those who suffered cramp and those that don’t.